Overview
Scabies is a common skin condition caused by a tiny mite called Sarcoptes scabiei. The mite burrows into the top layer of the skin, causing itching and a rash. Scabies is highly contagious and can spread easily through close physical contact or through sharing personal items such as clothing or bedding. Children are particularly susceptible to scabies, and it is important to be aware of the symptoms, causes, treatment, and prevention of this condition.
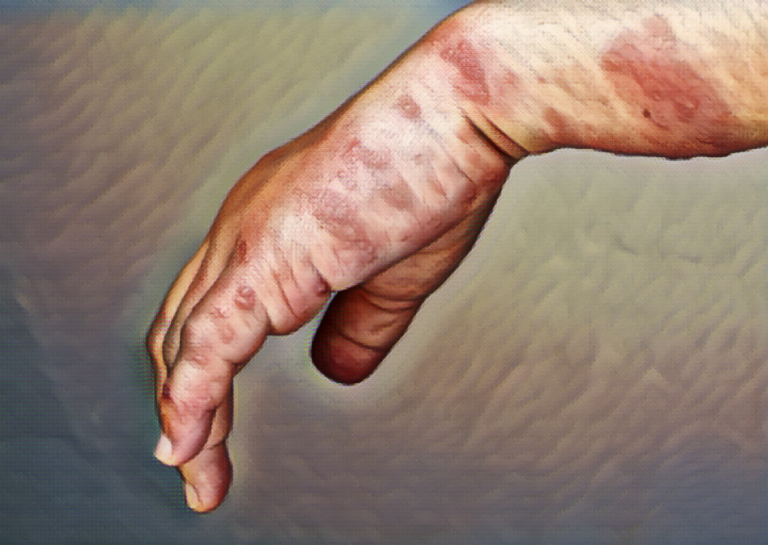
Symptoms
The symptoms of scabies can take up to four to six weeks to appear after initial infection. The most common symptoms include intense itching, especially at night, and a rash made up of small, red bumps or blisters. The rash may appear in areas such as the wrists, fingers, elbows, armpits, and around the waist, but it can appear anywhere on the body. In children, the rash can also appear on the scalp, face, and soles of the feet.
Other symptoms that may occur in children with scabies include:
- Sores caused by scratching the itchy rash
- Scaling of the skin
- Swelling of the lymph nodes
- Crusty areas on the skin
Causes
Scabies is caused by the Sarcoptes scabiei mite, which is a tiny, eight-legged creature that can only be seen with a microscope. The mite burrows into the top layer of the skin and lays its eggs, causing an allergic reaction that leads to itching and a rash. Scabies can be transmitted through close physical contact with an infected person or through sharing personal items such as clothing or bedding.
Risk factors for scabies include:
- Crowded living conditions
- Poor hygiene
- Lack of access to healthcare
- Exposure to infected individuals
Treatment
Treatment for scabies typically involves the use of medicated creams or lotions that are applied to the skin. These medications work by killing the mites and their eggs, and they are available by prescription from a healthcare provider. Commonly prescribed medications include permethrin, crotamiton, and lindane. In some cases, oral medications such as ivermectin may also be prescribed.
It is important to follow the instructions for use of the medication exactly as prescribed by the healthcare provider, and to avoid scratching the rash to prevent further irritation and infection. In addition, all clothing, bedding, and personal items that have come into contact with the infected person should be washed or dry cleaned to prevent re-infestation.
Prevention
Preventing scabies is primarily focused on avoiding close physical contact with infected individuals and practicing good hygiene.
- Wash hands frequently
- Avoid close contact with infected individuals
- Keep fingernails short and clean to reduce the chance of infecting oneself
- Clean and sanitize all personal items, bedding, and clothing that may have come into contact with infected individuals
It is also important to be aware of the signs and symptoms of scabies, and to seek treatment as soon as possible if an infection is suspected.
Citations
- American Academy of Dermatology. (2021). Scabies. https://www.aad.org/public/diseases/contagious-skin-diseases/scabies
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2021). Scabies. https://www.cdc.gov/parasites/scabies/index.html